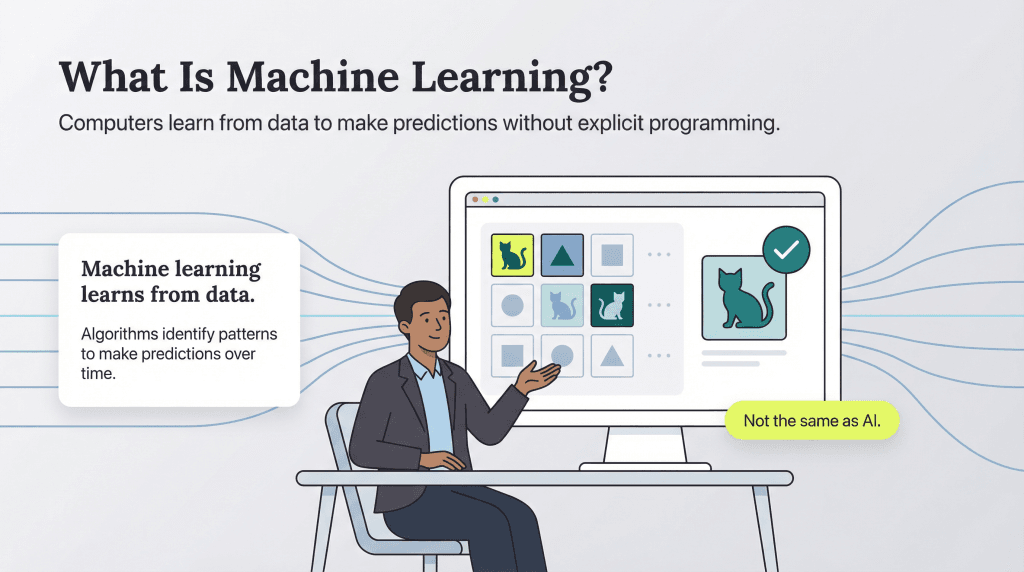
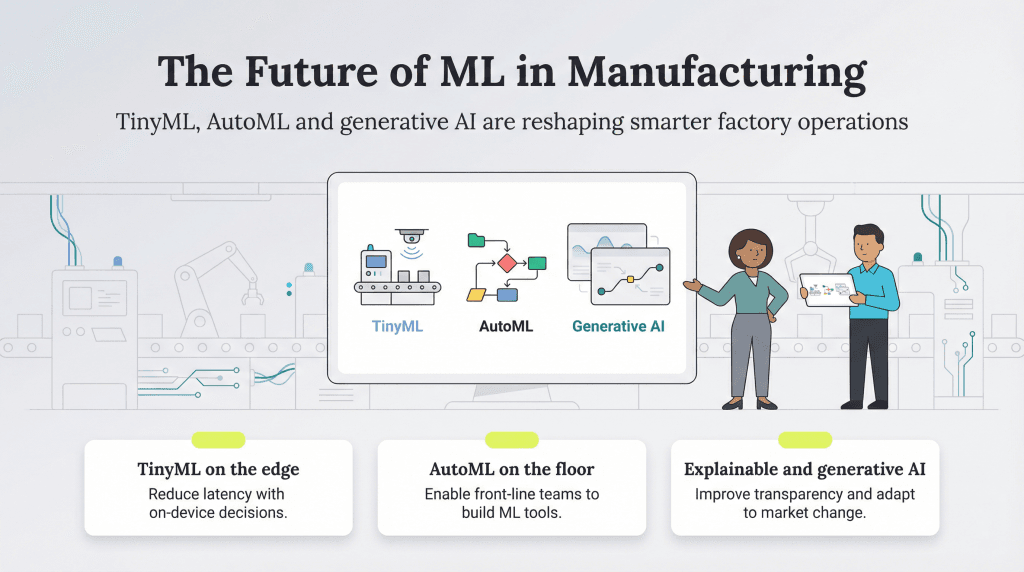
Machine learning is proving to be a game-changer for manufacturers, helping improve product quality, reduce waste and prevent costly equipment failures by analyzing massive datasets that would be impossible for humans to process manually. We’ll explain how machine learning works, explore the key ways it’s transforming manufacturing operations and look at what the future may hold.
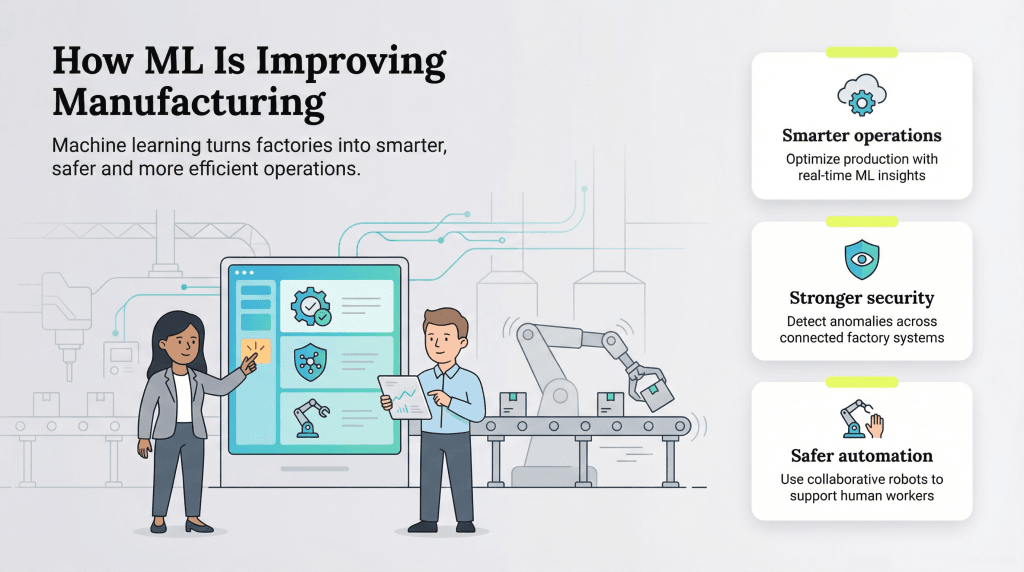
How ML is improving manufacturing
Manufacturers are increasingly using machine learning because it delivers highly accurate predictions and can anticipate production anomalies before they occur.
John Rossman, managing partner at technology and innovation consultancy Rossman Partners, says ML’s impact on manufacturing will be significant. “The adoption of ML in manufacturing is setting the stage for a future where efficiency, precision and customer-centric innovation thrive,” Rossman explained. “As manufacturers invest in these capabilities, the true differentiator will be their ability to ‘think big, but bet small’ and take a systematic approach to experimentation.”
Consider the following five ML use cases that are transforming manufacturing today.
1. ML is improving general manufacturing processes.
Manufacturers are using ML-based solutions across the entire production cycle. These data-driven systems help uncover hidden inefficiencies in existing operations, including production bottlenecks, underperforming lines and quality control gaps that can impact profitability.
The combination of ML and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies — such as sensors — creates powerful new opportunities. Together, they give manufacturers deeper visibility into logistics, inventory, business assets and supply chain operations. This integration supports “smart factory” environments, where data reveals high-value insights related to production speed, packaging integrity and distribution routing.
A well-known example is Intel’s use of ML in microchip manufacturing. During production, the company captures high-resolution images of the thin silicon wafers used to make each chip. ML then scans those images for defects, such as scratches or bubbles, that are easy for human inspectors to miss.
When an anomaly is detected, the system can immediately pause production, allowing teams to identify and correct the issue before additional defective chips are produced.
VR technology in manufacturing is being used to improve inventory management, product design and assembly, maintenance training and factory floor planning.
2. ML is transforming product development.
Product development is one of the most widely adopted use cases for machine learning. Launching successful, unique new products often requires analyzing large volumes of historical data alongside current market trends, which is something ML is well-suited to handle.
ML solutions help manufacturers gather and analyze consumer data to better understand demand, uncover unmet needs and identify new business opportunities. These insights allow companies to refine existing products and develop new ones, opening additional revenue streams while reducing the risks tied to innovation.
ML is particularly effective at lowering product development risk because its insights inform early planning decisions, leading to more confident and data-backed choices.
Val Neicu, CEO and co-founder of SmartSKN, shared how her company uses ML to transform skincare product development. “By analyzing vast amounts of consumer skin data, ML enables us to create hyper-personalized formulations that align precisely with each customer’s needs, reducing the risks associated with launching new products,” Neicu explained.
At SmartSKN, customers use an AI-powered dermoscope to assess their skin condition. ML then helps formulate a personalized skincare product tailored to each customer’s profile. “Our manufacturing system is powered by ML to produce products on demand, minimizing waste and ensuring efficient inventory management,” Neicu added. “This dynamic approach allows us to respond in real time to customer demands without overproducing.”
This approach improves production efficiency while delivering a highly interactive customer experience that blends advanced technology with convenience.
3. ML is advancing quality control.
ML can improve final product quality significantly in two ways:
- It detects product anomalies: ML algorithms monitor products as they move along the assembly line, flagging defects before items are shipped to distributors. Computer vision tools can detect microscopic flaws that are easy for human inspectors to miss.
- It supports predictive maintenance: Using IoT devices and ML applications, manufacturers can analyze equipment availability and performance throughout the production process. According to the Operations & Maintenance Best Practices Guide from the U.S. Department of Energy, predictive maintenance programs can reduce downtime by 35 percent to 45 percent and increase production by 20 percent to 25 percent compared to less advanced maintenance approaches.
A real-world example comes from Carlsberg, which uses ML-powered quality control to detect subtle taste differences between beers that human testers often miss. During production, the company collects detailed data on each beer’s aroma and flavor profile. ML models analyze this data to flag inconsistencies or defects much earlier in the process, reducing the number of subpar products leaving the factory and helping ensure consistent quality for customers.
General Electric offers another example of ML-driven quality control at scale. The company has deployed ML-based tools across more than 100,000 assets spanning industries such as aerospace, power generation and transportation. These systems identify early warning signs of manufacturing anomalies and provide long-term prognostics to help estimate equipment performance and lifespan.
Consistent
product quality creates a virtuous cycle: It builds trust and
customer loyalty, encourages word-of-mouth recommendations and lowers maintenance and customer support costs over the life cycle of a well-made product.
4. ML is enhancing security.
ML solutions operate across applications, operating systems, networks, cloud computing platforms, on-premise systems and other potential attack surfaces. This level of connectivity makes device and data security a top priority for modern smart factories. ML also plays an important role in zero trust security (ZTS), a framework that tightly controls access to systems and data to reduce exposure to threats and protect your business’s sensitive information.
ML strengthens security by analyzing user behavior and access patterns. It evaluates how individuals interact with protected data, which applications they use and how they connect to them. By enforcing strict access controls around digital assets, ML systems can detect unusual activity and trigger alerts or automated responses when anomalies occur.
As factories adopt more connected systems, security risks are rising alongside them. IBM’s 2025 X-Force Threat Intelligence Index shows that manufacturing was the most targeted industry for the fourth year in a row, accounting for 40 percent of all security incidents and leading all sectors in ransomware attacks. For manufacturers, the message is clear: Stronger safeguards are no longer optional.
5. ML is fueling robot technology.
AI enables robots to handle routine tasks that are complex, repetitive or dangerous for humans. With ML capabilities, robots can move beyond traditional assembly-line roles and take on more intricate manufacturing processes.
Manufacturers are increasingly adopting collaborative robots, or “cobots,” that are designed to work safely alongside human employees. That’s the approach taken by KUKA, a German robotics manufacturer majority-owned by a Chinese parent company. KUKA builds industrial robots meant to operate safely next to people, including its LBR iiwa model. Advanced sensors allow the robot to handle complex tasks while sharing workspace with human workers, improving both productivity and safety.
Peter Gorm Larsen, vice head of section at Aarhus University and coordinator of the RoboSAPIENS project, is pursuing similar goals through academic research.
“Adaptive robots usually behave by continuously monitoring their environment, analyzing the data collected, changing [their] plans, if needed, and then executing the new plans, accumulating knowledge as it goes along,” Larsen explained. “This is called a MAPE-K (Monitor-Analyze-Plan-Execute-Knowledge) control loop.”
However, Larsen noted that this approach still lacks a built-in mechanism to verify whether certified safety and trustworthiness guarantees are preserved as robot behavior changes. “The future of safety and trustworthiness of automated industrial robots comes when the robot can change its behavior while maintaining — or even increasing — its expected performance and staying at least as safe and robust as before it made the change,” he said.
Larsen’s work on the RoboSAPIENS project focuses on developing the underlying technologies needed to make adaptive robotics safer and more efficient. Over time, these advances could help reduce human error, increase productivity and deliver value across the manufacturing supply chain.
ML and AI have an important role in modern manufacturing, but humans remain essential. When evaluating automation opportunities, many manufacturers find the best results come from combining human judgment with intelligent machines, instead of choosing one over the other.