Keeping your data, customers, staff and assets safe is critically important. Every time a business suffers an intrusion, theft or damage, fixing the situation costs money. And, if security incidents happen too often, they can threaten a company’s survival. However, many entrepreneurs struggle to find the time and resources to give business security the attention it deserves.
The financial stakes have never been higher. According to IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.9 million in 2024, representing a 10% increase from the previous year and the highest total ever recorded. For many small businesses, a single data breach could be enough to strike a fatal blow, which is why putting the right security measures in place is worth the time, cost and effort.
How security supports business growth
Business security supports business growth by improving customer loyalty and trust, preventing costly data breaches, and ensuring regulatory requirements are met. It also ensures a business can continue its operations unhindered by data breaches and other cyberattacks.
Enhanced customer trust
Strong security measures directly translate to business opportunities and revenue growth. Research shows that 87% of consumers will take their business elsewhere if they don’t trust a company to handle their sensitive data responsibly.
Cost avoidance and improved ROI
Organizations that extensively deploy security AI and automation save an average of $2.22 million compared to those without these technologies, according to IBM’s research. This represents a significant return on security investment (ROSI) that directly contributes to profitability and growth capital.
Regulatory compliance and market access
Compliance with industry regulations like GDPR, SOX, and PCI DSS isn’t just about avoiding fines—it’s about accessing new markets and business opportunities. For example, PCI DSS 4.0 compliance, which became mandatory in April 2024, is essential for any business accepting credit card payments. Non-compliance can result in significant fines and loss of payment processing capabilities, directly impacting revenue growth.
Operational continuity and productivity
Breaches involving stolen or compromised credentials take an average of 292 days to identify and contain, according to IBM’s research. That’s nearly 10 months of potential disruption. By implementing strong security measures, businesses ensure continuity and maintain productivity while competitors may struggle with downtime and recovery costs.
Cybersecurity: Defending your digital assets
With constant business internet connections, thieves don’t have to break into your premises to steal vital company assets like customer data, intellectual property and other sensitive information.
The threat landscape has evolved dramatically in recent years. According to Verizon’s 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, human error is a factor in 74% of data breaches. Stolen or compromised credentials account for 86% of all breaches, making them the most common initial attack vector.
Fortunately, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk. Organizations using extensive security AI and automation can identify and contain breaches 100 days faster than those without these technologies, according to IBM’s research.
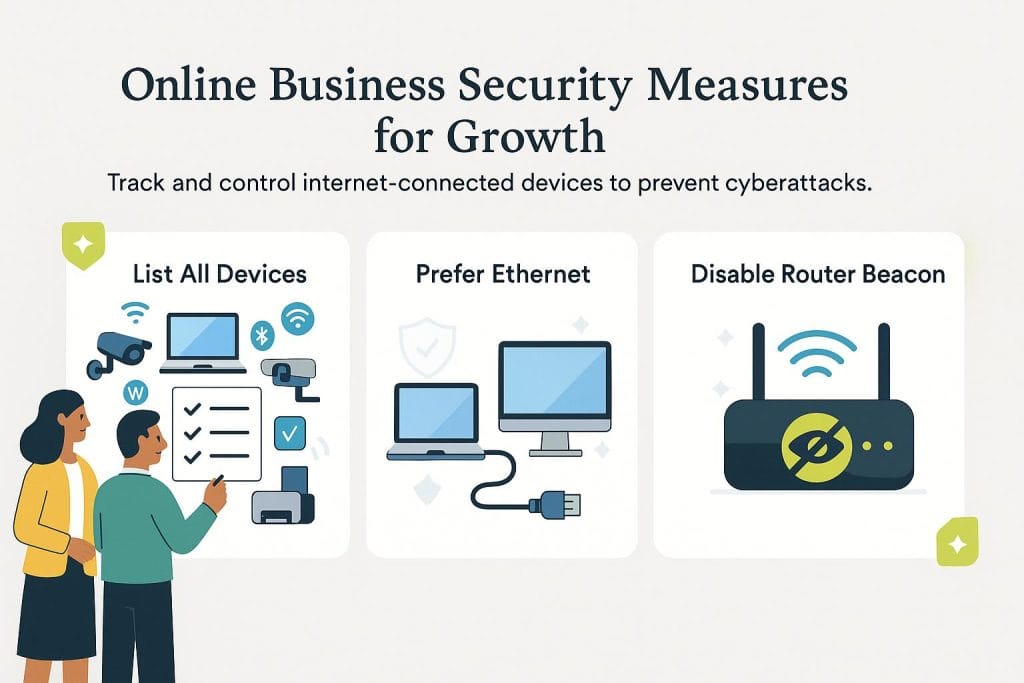
Network security and device management
Any device connected to your IT network that can access the internet is a vulnerability. To stay on top of potential threats, create a list of devices that can connect to business Wi-Fi. Include everything that connects wirelessly, including security cameras and shared printers. Deny access to any unregistered device trying to connect.
Additionally, consider implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0. The updated framework, released in February 2024, provides comprehensive guidance for organizations of all sizes. It introduces a new “Govern” function alongside the traditional five functions (Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond and Recover), emphasizing the importance of cybersecurity governance aligned with business objectives.
Eliminate risky physical media
Despite declining usage, many users still like CD-ROMs, USB sticks and flash drives. Physical media devices have many security issues and are easy to lose and steal.
If a colleague uses physical media for work and personal purposes, that can be a problem. They may unwittingly download a file containing malware that could infect the office network when plugged into a computer at work.
Consider using a cloud storage service like Dropbox or Google Drive to share files between colleagues.
Comprehensive employee training programs
In most cases, employees are unaware — and never realize — that they’ve done something that threatens their company’s data security. The most common incident is clicking on links in phishing emails, which may introduce malware used to steal sensitive information.
Training can reduce the likelihood an employee’s actions compromise the company’s cybersecurity. Companies that regularly train employees on phishing threats see a 50x return on investment on cybersecurity training, according to the Ponemon Institute. This makes employee education one of the most cost-effective security investments a business can make.
“Start with regular training sessions that are simple and engaging, using real-life examples to illustrate potential threats,” said Adhiran Thirmal, senior solutions engineer at cybersecurity firm Security Compass.
Additionally, employees should feel comfortable reporting suspicious incidents. “Encourage a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activities without fear of reprimand,” Thirmal said. “Recognize and reward proactive behavior, and make sure that leadership consistently emphasizes the importance of cybersecurity in everyday operations.”
Investing in employee training is crucial for business security. Develop an effective cybersecurity training program and monitor your team to ensure they're putting their knowledge into action.
Advanced threat detection and response
Cybercriminals take the path of least resistance when targeting small businesses. The more complicated a system is to crack, the less attractive it is for a hacker to spend the time and effort to infiltrate it.
Consider investing in an intelligent firewall solution as a minimum security measure for your business. Firewalls can detect and block suspected traffic, shutting down an attack immediately.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions represent the next evolution in threat detection. IBM’s research shows that 44% of organizations have implemented XDR solutions, and these organizations accelerate detection and containment of data breach incidents by approximately one month compared to those without XDR solutions.
Secure remote connectivity
Earlier, we mentioned that Wi-Fi is often insecure and that, where possible, employees should avoid it. If employees must access the internet outside the office in a public space on their device, they should use 4G or 5G connections instead.
Cybercriminals often create spoof Wi-Fi access points using the venue’s name to deceive users into connecting. Once connected, data sent to and from the device is susceptible to interception.
If an employee must use Wi-Fi, insist they connect via a VPN. The best VPN services encrypt all data, so even if the employee uses a spoofed network, the intercepted data will be indecipherable to the hacker.
“Encryption and VPNs are vital for keeping data secure, especially when it’s in transit or accessed remotely,” Thirmal said. “VPNs add a layer of security by encrypting data and verifying the identity of users, even on public or unsecured networks.”
To ensure
e-commerce website security for your online store, choose a secure e-commerce platform, implement SSL certificates and use a virtual private network (VPN).
Physical security: Protecting your foundation for growth
It’s not just cybersecurity that matters for your business’s survival; securing your business’s physical location and assets is crucial, as well.
“I’ve seen how physical security directly supports the growth of businesses,” said Eugene Klimaszewski, CEO of electronic security firm Mammoth Security. “Your assets are better protected, and your losses are lower, meaning you have more money to invest in growth.”
Consider the following best practices for your business’s physical security.
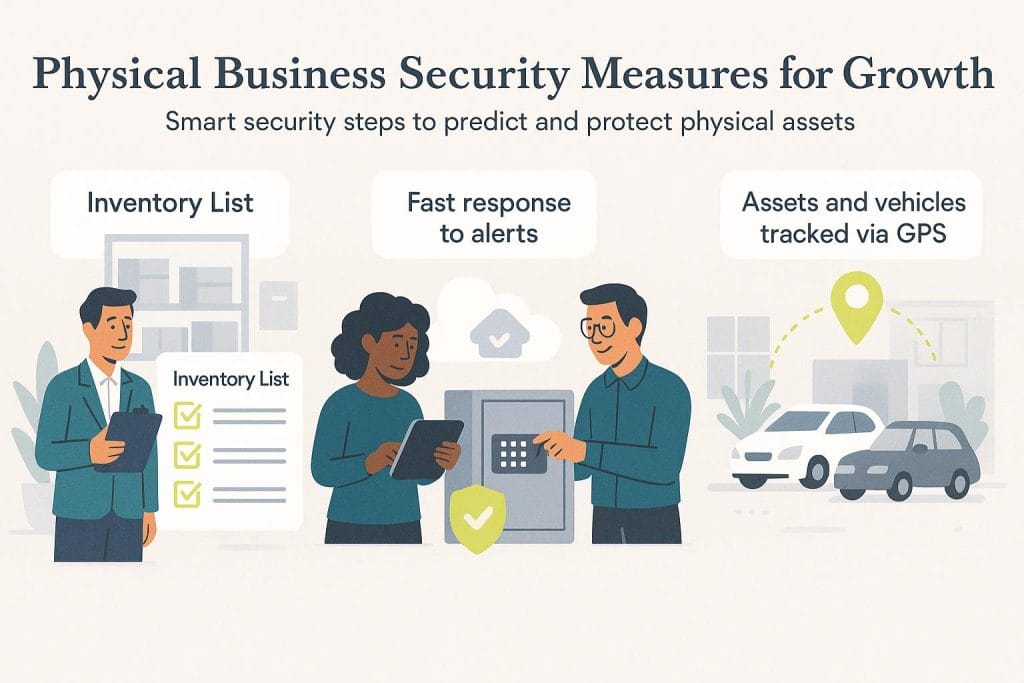
Asset tracking and monitoring
Tag your vehicles and assets with GPS trackers, so you always know where they are. Sensors transmit location information frequently, allowing you to see their positions in near real time. [Read related article: How to Choose a GPS Fleet Tracking Solution]
Secure storage for valuable equipment
Assets like desktop computers, tablets, laptops, flat-screen displays and projectors are portable and easy for thieves to conceal if you don’t have door security.
While the face value of this equipment might not always be high, devices may contain proprietary and private data and information. Some devices may automatically log in to your company network, putting your wider IT network at risk.
Consider creating safe rooms in convenient locations for co-workers to store this type of equipment overnight to help keep company data and assets safe.
Professional security services
On-site security guards are a proven theft deterrent. If you’re concerned about theft, security guards can conduct door checks as people (customers, visitors, employees and more) come and go. Security guards can protect stock in big warehouses just as much as they can in a retail outlet.
If the cost of 24/7 guards is too high, consider hiring a mobile patrol for when your premises are closed. They’ll be on-site immediately if a burglar alarm goes off or CCTV detects movement when there should be no one in the building.
Additionally, mobile patrols can be your keyholders if there’s a break-in. They can let police in to investigate a potential crime scene without having to wait for the company to open.
Advanced access control systems
Determined criminals can beat standard commercial-build locks. Most commercial rental properties will allow tenants to change locks once the owner gets a key.
Replacing a location’s standard bolts with more sophisticated locks should be among the first changes a business makes to help ensure its continued security.
A range of access control systems can restrict entry and serve as visitor management systems. Klimaszewski says business owners should choose an access system that suits their property’s size and safety needs. “For small to medium businesses, key card systems are a smart pick, costing between $1,000 to $3,000 per door,” Klimaszewski suggested. These straightforward access control systems use RFID-enabled key card fobs that unlock the door when held up to the reader.
Bigger organizations or more complicated setups may need more extensive access control measures. “For those overseeing larger facilities or requiring enhanced security measures, investing in biometric systems such as fingerprint or retinal scans is advisable, despite the potential cost exceeding $10,000 per installation,” Klimaszewski advised.
To maximize your cybersecurity budget, Klimaszewski recommends that business owners “weigh the sophistication of the system against their genuine security needs to ensure they’re making a cost-effective decision.”
Many access control systems run off databases with codes specific to each person. You can generate new cards and biometric passes using your vendor’s software. You can also deactivate existing access control permissions to deny someone entry.
Tailgating — when an unauthorized user sneaks in behind an authorized one — is a top access control concern. Some
business security system features can track when more than one person enters. Security guards can then deal with the issue.
Modern surveillance technology
For a time, CCTV lost its power as a deterrent. Video from security cameras was blurry, which made identification challenging, and footage wasn’t presentable as evidence in court cases.
Today, companies put up signage to warn intruders that their CCTV system records in HD or 4K. High-speed internet has also enabled HD and 4K picture transmission to remote control rooms. If an event is detected, a control room operator can view it and judge whether to inform a mobile patrol or the police.
Klimaszewski recommends that business owners select cameras with at least 1080p resolution to capture every detail crisply. “Fuzzy footage can disrupt your security effectiveness, complicating both immediate actions and subsequent analyses,” Klimaszewski cautioned. “High-def cameras are worth the investment for clear-cut evidence and stronger security.”
Another significant CCTV development is the use of AI to alert controllers to unusual behavior and incidents in real time. Instead of watching a bank of screens for hours, the software captures video of unusual behavior and presents it to the control room operator, who decides what action to take.
Monitored alarm systems
Much like with car alarms, people no longer react to burglar alarm activations. In recent years, the market has shifted toward 24/7 monitored alarm systems. Klimaszewski says these systems can step up your security game. “When trouble hits, these alarms alert you and the security team, who can respond swiftly, often quicker than the police,” Klimaszewski explained. “The added security and possible business insurance discounts make these alarms a must-have for a solid physical security plan.”
If mobile patrols get to the scene and discover the breach report was correct, they can then send for a police response.
Document security protocols
Documents left on employees’ desks are easy to remove and may contain sensitive commercial information you want to keep within your company. Ask co-workers to store documents in locked drawers at their desks when they’re not using them. Also, have them retrieve their printouts immediately when utilizing a shared printer.
Consider digitizing documents in an online document management system. This means scanning, indexing and uploading documents to a secure cloud for easy retrieval as needed. For added security, remember to shred all physical documents after uploading them.
Business security system costs depend on your required features, such as video surveillance systems, intrusion-detection alarms and electronic access control systems.
Cost-benefit analysis: The financial case for security investment
Understanding the return on investment for cybersecurity is crucial for business growth planning. The numbers in IBM’s research are compelling:
- Average data breach cost: $4.88 million
- Average ransomware attack cost: $4.99 million per incident
- Cost savings with AI-driven security: $2.22 million per breach
- Healthcare industry average: $9.77 million per breach
Calculating your security ROI
The formula is straightforward:
(Money saved due to security measures – Security investment cost) ÷ Security investment cost × 100 = ROI percentage
For example, a small business investing $33,500 in cloud-based security that prevents just one breach costing $138,230 would realize an ROI of $104,730, representing more than 300% return on investment.
Insurance and regulatory benefits
Organizations with robust cybersecurity measures often qualify for reduced cyber insurance premiums, providing direct financial benefits. Additionally, maintaining compliance with regulations like PCI DSS, GDPR, and industry-specific requirements prevents costly fines and enables business expansion into new markets.
Implementation roadmap: A step-by-step security enhancement plan
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-2)
- Conduct security assessment using NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 as a baseline
- Implement basic access controls (multi-factor authentication, strong password policies)
- Deploy endpoint security on all devices
- Establish backup procedures with regular testing
- Create incident response plan with clear roles and communication protocols
Phase 2: Enhancement (Months 3-4)
- Deploy advanced threat detection (XDR or SIEM solutions)
- Implement employee training program with quarterly updates
- Establish vendor security assessments for third-party risk management
- Deploy network segmentation to limit potential breach impact
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) tools
Phase 3: Optimization (Months 5-6)
- Deploy AI-driven security automation for threat detection and response
- Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments
- Implement continuous monitoring and security metrics dashboard
- Establish security governance committee for ongoing oversight
- Review and update security policies quarterly
Ongoing maintenance
- Monthly security awareness training
- Quarterly vulnerability assessments
- Annual penetration testing
- Continuous monitoring and threat intelligence updates
- Regular review of security metrics and ROI calculations
Security as a growth catalyst
Your business’s future depends on your ability to protect your assets, people and reputation from bad actors, both internal and external.Start with the fundamentals: implement the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0, invest in AI-driven security automation, and create a comprehensive employee training program. In an increasingly digital world, trust is the ultimate currency, and security is how you earn it.